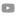
Manica rubida is a highly aggressive species of ant native to most central and southern European countries. These ants are typically found at elevations between 900 and 2000 meters. They are known for their powerful sting and aggressive hunting behavior, making them unsuitable for individuals with allergies to ant stings.
Manica rubida
Colony Structure and Reproduction: Manica rubida ants are semi-claustral, meaning the queen hunts during the founding stage as she lacks food stores to raise her nanitics. Queens range from 10-13mm in size, while workers measure between 6-9mm. Colonies can reach a few thousand workers once mature but tend to grow relatively slowly.
Size and Appearance: The queen ants of Manica rubida are relatively large, measuring 10-13mm, while the worker ants are smaller, ranging from 6-9mm. These ants have a robust build and are known for their powerful stings, which they use effectively in hunting and defense.
Feeding Behavior: Manica rubida ants are not picky eaters and require a protein-rich diet to support their brood. They primarily feed on insects such as mealworms, crickets, cockroaches, and fruit flies. Additionally, they need a sugar source like honey, sugar water, or fruit to fuel the workers' energy needs.
Activity and Hunting: These ants are active hunters, capable of preying on both live and dead insects. The queen, being semi-claustral, will forage and hunt for food during the founding stage. Their aggressive nature and powerful sting make them efficient predators.
Temperature and Humidity: Maintaining an optimal environment is crucial for Manica rubida. The nest should be kept very humid, with regular hydration and a decent external water source. These ants do not require additional heating and can be kept at room temperature. However, heating can speed up brood progress.